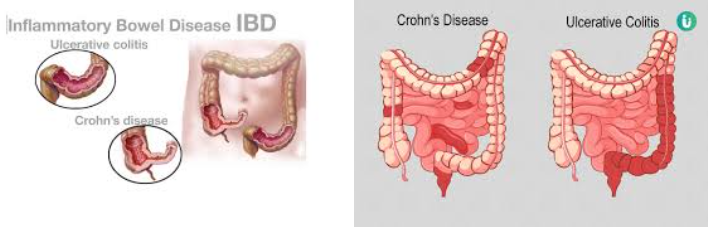
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a group of autoimmune conditions characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. This inflammation leads to a myriad of symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhoea, weight loss and malabsorption that increases the nutritional needs. People with inflammatory bowel disease, for example, Crohn’s ulcerative colitis, find that certain foods or products trigger flares, which worsens the disease.
A diet low in fermentable oligo-di-monosaccharides and polyols, or FODMAPs, is beneficial for managing IBD. This diet eliminates a wide variety of carbohydrates to abate symptoms such as diarrhea and constipation. People with Crohn’s disease face difficulty tolerating dairy products because of intolerance to milk (lactose intolerance). They also are more prone to nutritional deficiencies because of the lack of nutrient absorption in the intestine. Ulcerative Colitis(UC) is a chronic autoimmune disease causes inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the colon, or large intestine. The inflammation sometimes occurs only in the lower part of the colon and the rectum, but it may also affect the entire colon. The most common symptoms of UC are diarrhea and bleeding. . The course of UC is cyclical in nature, often with periods of active disease alternating with periods of symptom free remission. People with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis often find it difficult to get their daily nutritional needs because of their disease. Vitamins and other nutritional supplements can help provide some of the necessary nutritional needs to people with IBD . A low-residue diet helps to relieve flare-ups.
At Pro Health Diet Clinic, the targeted nutrition therapy is aimed at reducing inflammation through diet which is highly underutilized in the standard treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
Consultation Fee: Rs. 1500/-
Diet chart charges extra